What is Arad History? Understanding Its Impact and Significance

Arad’s story is much older and more layered than most cities in Romania. Recent studies show continuous settlement from the Neolithic era, stretching back thousands of years along the Mures River. You might think such ancient roots would make Arad a relic frozen in time. Instead, that same history fueled a vibrant mix of cultures, languages, and ideas that still define the city today.
Table of Contents
- The Historical Roots Of Arad: A Timeline
- Ancient Foundations And Early Settlements
- Medieval Transformations And Cultural Dynamics
- Modern Era And Regional Significance
- Cultural Significance Of Arad Through The Ages
- Multicultural Urban Fabric
- Intellectual And Artistic Contributions
- Economic And Social Transformation
- Arad’s Role In Regional Development And Politics
- Administrative Reorganization And Institutional Development
- Economic Strategy And Regional Integration
- Political Transformation And Territorial Dynamics
- Key Events And Figures In Arad History
- Religious And Demographic Transformations
- Ethnic And Cultural Leadership
- Economic And Institutional Pioneers
- Preservation And Promotion Of Arad’s Historical Legacy
- Architectural And Cultural Conservation
- Digital Documentation And Research
- Community Engagement And Cultural Interpretation
Quick Summary
| Takeaway | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Arad has a complex historical background. | The city’s history includes prehistoric settlements, Roman influences, and diverse cultural interactions. |
| Cultural diversity shapes Arad’s identity. | Arad is characterized by Romanian, Hungarian, German, Serbian, and Jewish communities, influencing its social life. |
| Arad played a key role in modernization. | In the 19th and 20th centuries, it became a center for industrial growth and cultural exchange in Romania. |
| Preservation of heritage is vital for Arad. | Efforts include digital documentation and community engagement to maintain the city’s historical legacy. |
| Strategic location enhances Arad’s significance. | Its position has historically made it a crossroads for trade, culture, and political dynamics in the region. |
The Historical Roots of Arad: A Timeline
Arad’s historical landscape represents a complex tapestry of cultural interactions, migrations, and transformative periods that have shaped its remarkable identity. Located in western Romania, this city has witnessed significant historical developments spanning multiple centuries and civilizations.
Ancient Foundations and Early Settlements
The region surrounding Arad demonstrates human settlement patterns dating back to prehistoric times. Archaeological evidence suggests continuous habitation from the Neolithic period, with early communities establishing themselves along the Mures River. Encyclopaedia Britannica confirms that these early settlements were strategically positioned, benefiting from the river’s resources and fertile agricultural lands.Key historical periods of early settlement include:
- Dacian tribal communities establishing initial territorial control
- Roman imperial expansion and subsequent cultural influences
- Migration period interactions with various ethnic groups
Medieval Transformations and Cultural Dynamics
During the medieval era, Arad emerged as a significant administrative and strategic location. The city experienced complex political transitions, transitioning between Hungarian Kingdom control, Ottoman Empire influence, and Habsburg imperial governance. These shifts fundamentally transformed Arad’s demographic and cultural composition.Important medieval developments included:
- Establishment of critical trade routes
- Development of multicultural urban infrastructure
- Integration into broader regional political systems
Modern Era and Regional Significance
By the 19th and 20th centuries, Arad had evolved into a crucial economic and cultural center in western Romania. The city played a pivotal role during national modernization movements, contributing significantly to Romania’s industrial and intellectual development. Wikipedia highlights Arad’s importance as a nexus of cultural exchange and economic innovation during this transformative period.The historical trajectory of Arad reflects a microcosm of broader regional dynamics, demonstrating how geographical location and cultural interactions shape urban development across generations.To help clarify Arad’s varied historical roles and influences, the following table compares the city across its Ancient, Medieval, and Modern eras, highlighting the defining characteristics of each period.
| Historical Era | Key Characteristics | Notable Influences |
|---|---|---|
| Ancient | Neolithic settlements along Mures River | Dacian, Roman cultural impacts |
| Medieval | Strategic administrative hub, multicultural growth | Hungarian Kingdom, Ottoman, Habsburg |
| Modern | Center for industry, culture, and national reforms | Industrialization, modernization |
Cultural Significance of Arad Through the Ages
Arad represents a remarkable crossroads of cultural interactions, embodying a complex narrative of multicultural heritage that transcends traditional historical boundaries. Its cultural significance emerges from layers of historical experiences, demographic diversity, and unique geographical positioning.
Multicultural Urban Fabric
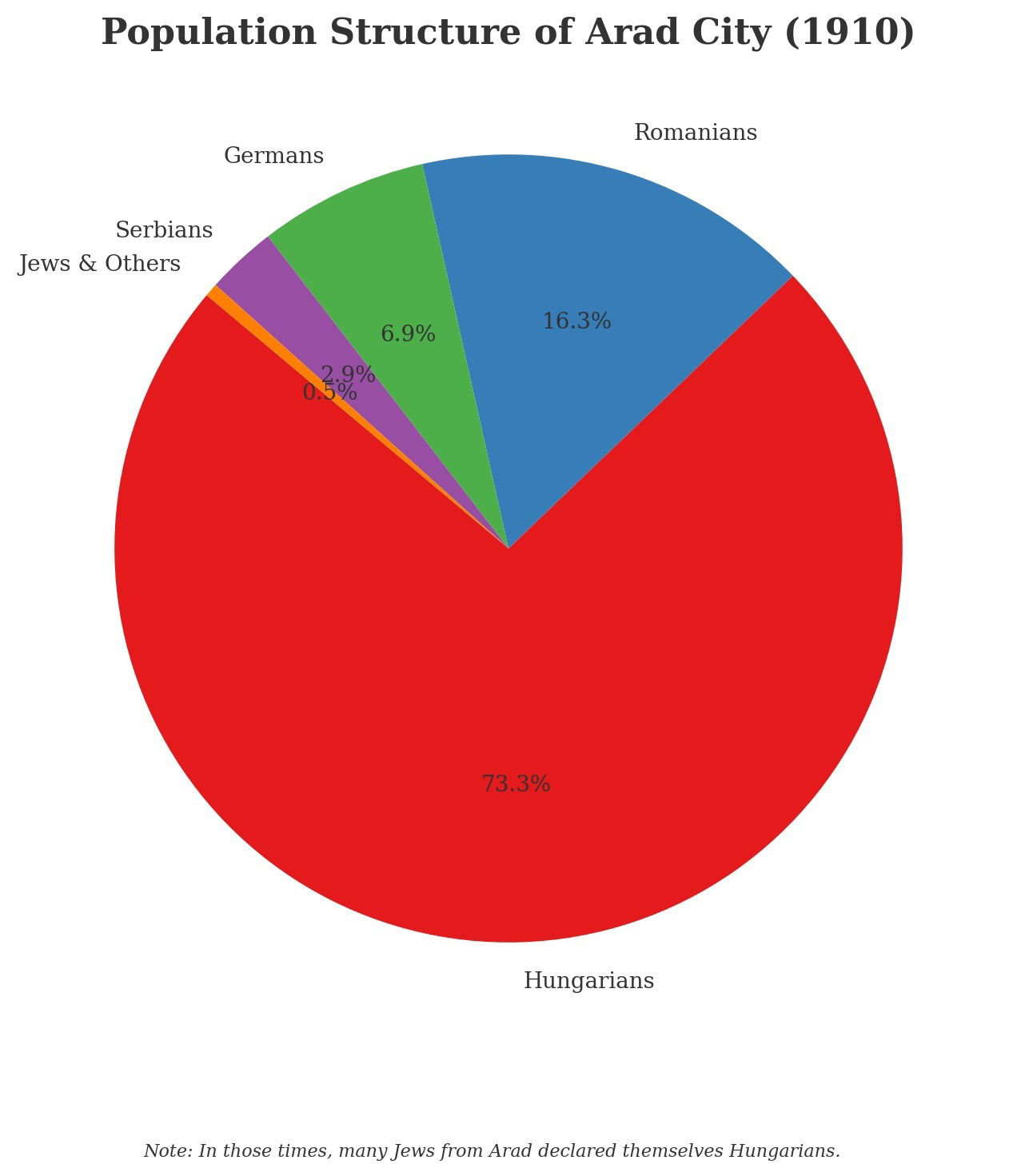
The city’s cultural landscape reflects an extraordinary blend of ethnic and linguistic diversity. The graph reveals how Arad developed as a melting pot of different communities, including Romanian, Hungarian, German, Serbian, and Jewish populations. This diverse composition fundamentally shaped the city’s social dynamics and cultural expressions.Significant aspects of Arad’s multicultural identity include:
- Linguistic diversity with multiple spoken languages
- Religious pluralism encompassing Orthodox, Catholic, Protestant, and Jewish traditions
- Architectural styles representing different cultural influences
Intellectual and Artistic Contributions
Arad emerged as an important intellectual center, nurturing significant cultural and artistic movements. The city became a critical hub for educational and creative endeavors, producing notable scholars, artists, and professionals who contributed to regional and national cultural development. Its educational institutions and cultural organizations played pivotal roles in preserving and promoting regional heritage.Key intellectual contributions included:
- Establishment of prominent academic and research institutions
- Preservation of multilingual literary and artistic traditions
- Development of cross-cultural academic and artistic networks
Economic and Social Transformation
Cultural interactions in Arad profoundly influenced its economic and social structures. The city’s ability to integrate diverse communities created a unique social environment that fostered innovation, tolerance, and economic dynamism. These cultural exchanges facilitated complex social negotiations and collaborative economic strategies that distinguished Arad from other regional urban centers.The cultural significance of Arad transcends mere historical documentation, representing a living testament to how geographical locations can become powerful symbols of human interaction, mutual understanding, and collective progress.

Arad’s Role in Regional Development and Politics
Arad has consistently played a strategic role in regional political and developmental dynamics, serving as a critical nexus of administrative, economic, and territorial transformation. Its geographical positioning and historical context have uniquely positioned the city as a significant driver of regional progress and political evolution.
Administrative Reorganization and Institutional Development
Eugen Ghita’s research reveals Arad’s pivotal role in administrative restructuring during the 18th century. Under Habsburg imperial governance, the city became a critical center for institutional innovation, implementing sophisticated administrative reforms that fundamentally reshaped regional governance structures.Key administrative developments included:
- Systematic territorial boundary redefinitions
- Implementation of centralized governance models
- Establishment of modern bureaucratic institutions
Economic Strategy and Regional Integration
Arad emerged as a crucial economic hub, strategically connecting different regional economic systems. Its development strategies focused on creating robust infrastructure, facilitating trade networks, and promoting industrial diversification. These approaches transformed Arad from a peripheral location into a significant economic center with far-reaching regional influence.Significant economic strategies encompassed:
- Development of transportation and communication networks
- Promotion of cross-border economic collaborations
- Investment in diverse industrial and agricultural sectors
Political Transformation and Territorial Dynamics
The political landscape of Arad reflected complex negotiations between different governance models, ethnic communities, and territorial ambitions. The city became a critical space where national and imperial political narratives intersected, creating a nuanced environment of political negotiation and cultural exchange.Through its continuous adaptation and strategic positioning, Arad demonstrated remarkable resilience in navigating complex political transitions, ultimately emerging as a symbol of regional dynamism and collaborative potential.
Key Events and Figures in Arad History
Arad’s historical narrative is marked by transformative events and remarkable individuals who shaped its trajectory through complex political, cultural, and social transitions. These pivotal moments and influential personalities have defined the city’s unique identity and regional significance.
Religious and Demographic Transformations
The region experienced profound demographic shifts as it transitioned from Ottoman to Habsburg governance, fundamentally altering its social structures and institutional frameworks.Significant demographic developments included:
- Establishment of Orthodox Episcopal centers
- Integration of diverse religious communities
- Systematic population resettlement and migration patterns
Ethnic and Cultural Leadership
Key historical figures emerged who played instrumental roles in Arad’s development, representing various ethnic and cultural backgrounds. These leaders facilitated complex negotiations between different community groups, promoting intercultural dialogue and collaborative progress.Notable leadership characteristics encompassed:
- Multilingual communication skills
- Diplomatic approach to community integration
- Vision for progressive urban development
Economic and Institutional Pioneers
Arad witnessed the rise of influential entrepreneurs and institutional builders who transformed the city’s economic and administrative landscape. These individuals introduced innovative approaches to commerce, education, and governance that positioned Arad as a forward-thinking urban center.The city’s historical narrative demonstrates how individual agency and collective endeavors can fundamentally reshape regional dynamics, creating a legacy of resilience, adaptation, and multicultural collaboration.
Preservation and Promotion of Arad’s Historical Legacy
Preserving Arad’s rich historical narrative requires sophisticated strategies that blend technological innovation, academic research, and community engagement. The city’s commitment to safeguarding its cultural heritage represents a dynamic approach to historical conservation and public education.
Architectural and Cultural Conservation
The Arad citadel study highlights the intricate process of preserving architectural landmarks that embody the city’s multilayered historical experience. Conservation efforts focus not just on physical restoration but on understanding the complex relationships between architectural elements and their historical contexts.Key architectural preservation strategies include:
- Detailed documentation of historical structures
- Innovative restoration techniques
- Integration of historical sites into contemporary urban landscapes
Digital Documentation and Research
Technological approaches have revolutionized how Arad’s historical legacy is documented and shared. Digital platforms enable comprehensive archival work, making historical resources accessible to researchers, educators, and the public while ensuring long-term preservation of fragile historical materials.Significant digital preservation initiatives encompass:
- Creation of comprehensive digital archives
- Digitization of historical collections
- Development of interactive research platforms
Community Engagement and Cultural Interpretation
Effective historical preservation extends beyond physical conservation, requiring active community involvement and meaningful cultural interpretation. Local institutions, museums, and educational programs play crucial roles in helping residents and visitors understand the significance of Arad’s historical narrative.The ongoing efforts to preserve and promote Arad’s historical legacy demonstrate a sophisticated understanding that heritage is not a static concept, but a living, evolving narrative that connects past experiences with contemporary identities and future aspirations.Below is a table summarizing the major strategies Arad has used to preserve and promote its historical legacy in the present day, outlining the primary approach, key actions, and intended outcomes.
| Preservation Approach | Key Actions | Intended Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Architectural Conservation | Restoration of historic buildings | Safeguard architectural heritage |
| Digital Documentation | Digitizing archives and collections | Increase accessibility, ensure longevity |
| Community Engagement | Educational programs, museum initiatives | Foster public understanding and pride |
Experience Arad’s Living History – Start Your Exploration Now
Have you felt the struggle of truly connecting with Arad’s rich multicultural story while researching its history? The article on “What is Arad History? Understanding Its Impact and Significance” highlights the complex layers of heritage, architectural treasures, and unique cultural interactions that have shaped this remarkable city. Yet, many readers hit a wall when trying to piece together authentic stories, access reliable research, or find firsthand insights that bring Arad’s dynamic past to life.Ready to go beyond the limits of surface-level facts? Unlock deeper knowledge and unique perspectives by exploring our curated books and blog about Arad at Arad.zone. Discover stories, visuals, and expert commentary that unravel the city’s transformation from ancient foundations to a vibrant multicultural hub. Visit Arad.zone now and start your personal journey into Arad’s living history before your next trip or research project.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the historical foundations of Arad?
Arad’s historical foundations date back to prehistoric times, with evidence of human settlement beginning in the Neolithic period along the Mures River, followed by the establishment of Dacian communities and later Roman influence.
How did medieval transformations impact Arad’s cultural dynamics?
During the medieval era, Arad became a strategic location under various rulers, including the Hungarian Kingdom and the Ottoman Empire. This led to significant political and cultural transitions, creating a multicultural urban infrastructure that shaped the city’s identity.
What role did Arad play during the 19th and 20th centuries?
In the 19th and 20th centuries, Arad emerged as a vital economic and cultural center, significantly contributing to Romania’s modernization and industrialization, establishing itself as a hub for intellectual and cultural exchange.
How is Arad’s historical legacy preserved and promoted today?
Arad’s historical legacy is preserved through architectural conservation efforts, digital documentation initiatives, and active community engagement, ensuring that its rich cultural heritage remains accessible and understood by future generations.